How Does a Heat Pump Work?
A heat pump works in winter by a process called thermodynamics which extracts heat from the outside air (even when it is cold outside) and transfers it into your home. In Summer, the process is reversed and a heat pump acts as an air conditioner (AC). A heat pump does this by extracting heat created inside your home and transferring it outside.
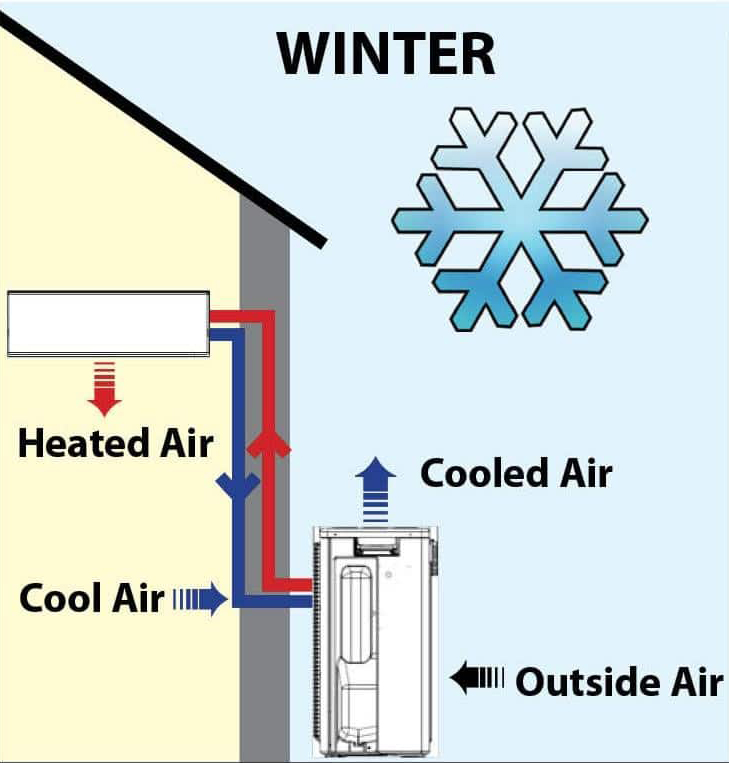
How does a heat pump work in winter?
In heating mode, the outdoor part of the heat pump, the heat exchanger is used to absorb heat from the outside air using refrigerant gas. The hot refrigerant is drawn through copper pipes to the indoor unit’s heat exchanger, the heat energy is then transferred inside the home via the indoor heat exchanger, in turn, warming the room.
The heating mode in more detail, heat transfer occurs when the working fluid in the evaporator from the outdoor air, turns into gas. The Heat pumps compressor increases the temperature and pressure of the gas and propels it into the heat pump condenser coils inside the heated area. Because the temperature of the gas is greater than the temperature in the room, heat transfer from the gas to the room occurs as the gas consolidates to a liquid. The working fluid is then chilled as it moves back through an expansion valve to the outside evaporator coils.
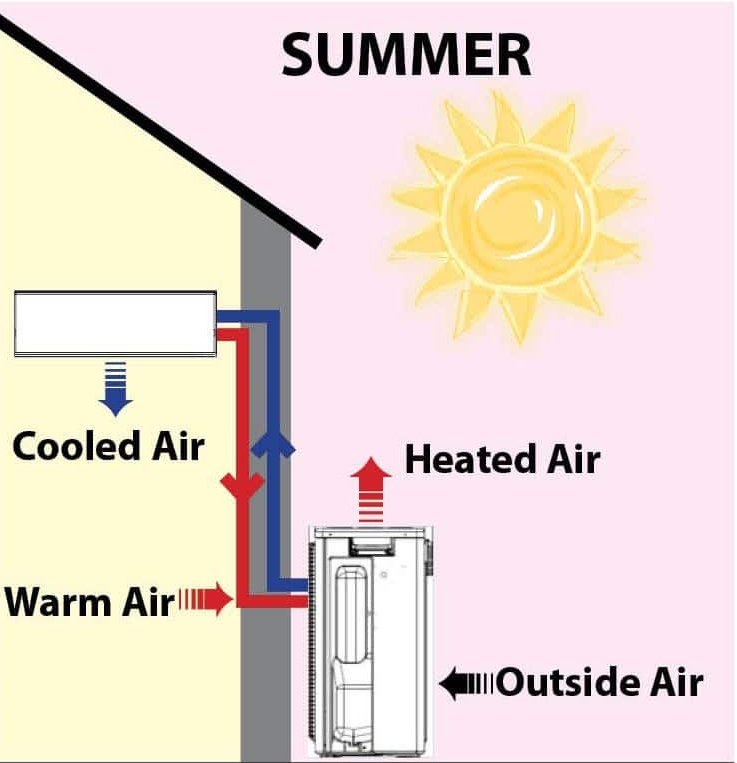
How does a heat pump work in Summer?
In cooling mode, the indoor units heat exchanger is used to absorb heat from the air inside the room using refrigerant gas. The refrigerant is then transferred to the outdoor unit through copper tubes and the heat energy is expelled into the surrounding air outside via the outdoor units heat exchanger.
How does a Split System heat pump work?
A split system heat pump has two major components, the condenser (located outside) that circulates refrigerant gas through the system and what is called an air handler (the indoor unit) that distributes the conditioned air.
How efficient is a heat pump?
Heat pumps are widely considered the most energy efficient form of heating large spaces and rooms such as lounges and living areas. This is demonstrated by producing between 3-4.5 kilowatts of heat for 1 kilowatt of power compared to an average electric heater which generates 2 kilowatts of heat for every kilowatt of power.
Our team offer an obligation free in-home assessment and can customise a heat pump solution right for your home.
Important Components of a Heat Pump
A conventional air source heat pump installation consists of two main components, an outdoor unit and an indoor air handler unit. Both the indoor and outdoor unit contain multiple sub-components.
Outdoor unit
The outdoor unit comprises a fan and a coil The coil operates as a condenser (cooling mode) or an evaporator (heating mode). The fan propels the outside air over the coil to help the heat transfer.
Indoor unit
Similar to the outdoor unit, the indoor unit, generally referred to as the air handler unit comprises a coil and a fan also. The coil functions as an evaporator (in cooling mode) and a condenser (in heating mode). The fan is responsible for passing air over the coil and throughout the ducts in your home.
Refrigerant
A heat pump refrigerant is a substance that receives and expels heat as it flows throughout the heat pump system.
Compressor
The Heat Pump compressor pressurises the refrigerant gas and propels it throughout the heat pump system.
Reversing Valve
The reverse valve part of the heat pump system reverses the flow of refrigerant, enabling the system to run in the opposite direction and switch between heating and cooling modes.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve functions as a metering mechanism, controlling the movement of refrigerant as it moves through the system, allowing for a decrease of pressure and temperature of the refrigerant.
Heat Pump and Air Conditioning FAQs
What heat pump works the best?
Heat pumps come in a variety of models and sizes. When deciding what heat pump to buy it is important to think about the location and the size of the area you are wanting to heat or cool.
Depending on the layout of your room you may be happy to have a heat pump sitting on your wall, or you may choose a more discrete option and go for a floor console, or a ceiling cassette.
You may also want to consider getting a heat pump with a star rating for further peace of mind you’re keeping your energy bills as low as you can.
What size heat pump do I need?
Getting the right size heat pump for the area you are wishing to heat or cool is the most important factor in its ability to work and the energy it consumes.
For a rough guide:
1. Room volume x 50 for a house with sufficient insulation
2. Room volume x 60 for a house without sufficient insulation
We strongly recommend booking a free home assessment and we can help you chose the right size unit for your home based on your homes thermal efficiency.
Where is the best place to put a heat pump?
Having your heat pump in the right location can make a big difference in the efficiency, and how a heat pump works, it can also affect the cost of the Heat pump installation too.
The first consideration is to make sure your heat pump can blow the air around the room unobstructed.
Secondly, all heat pumps need to link between the indoor and outdoor unit. Placing a heat pump on an external wall so we can run the piping directly to the external unit is ideal and will lower the install costs. Placing the unit on an internal wall may require a gravity pump and additional piping.
Our install price includes up to 5 metres of piping.
Will a heat pump save me money?
Most heat pumps have a COP rating of between 3 and 4.5. This means for one kilowatt of power used it will provide between 3 and 4.5 kilowatts of heat. The higher the COP the higher the efficiency of the unit.
In comparison most other conventional heaters have a COP rating of 1 or less, meaning for 1 kilowatt of power they will provide less than 1 kilowatt of heat.
While heat pumps are much more efficient, we still recommend turning heat pumps off when no-one is home to save power. All our heat pumps have 7 day timers so can be set to warm the house before you wake each morning or before you get home in the evening.

